
Test automation in 2026: Tosca in the cloud, agentic AI, and a smarter, more scalable future
Watch this webinar to hear two Tricentis experts discuss what’s...
Transformation Toolkit > Continuous Testing Framework

The Continuous Testing Framework (CTF) is designed to describe the roles, processes, skills, and tools organizations will need to establish modern testing practices. Collaboration is a key component of a high-performing development organization. It enables organizations to ensure their teams are working together effectively as they scale up their testing.
Consider how this collaboration would take place at the Team, Program, and Enterprise levels of an organization.

A team is defined as a group of people responsible for delivering a product. This team can work autonomously, making its own decisions about tools and processes. However, this situation is very rare—it tends to occur only in small organizations. The typical organization has a much more complex, connected IT landscape.

In a modern, agile development organization, there is normally more than one team involved in developing and testing applications. Having multiple teams allows an organization to build more complex products to meet ever-changing customer needs. When multiple teams are involved, responsibilities overlap and dependencies form.
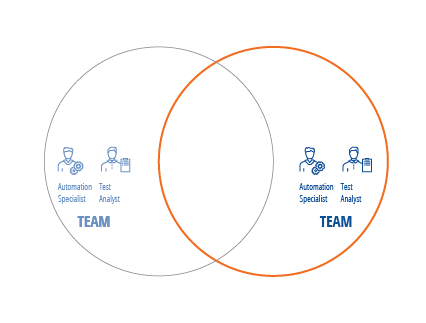
Business processes run across many different teams that must work together to deliver valuable features and working functionality. Dedicated roles at the Team level ensure that all your teams are speaking the same language and not working at cross-purposes.
Organizations should designate two roles that will execute testing at the Team level. Roles define the skillsets that are required and not the number of resources in the team. For example, one person can play multiple roles or multiple people can play the same role:
Your Automation Specialists and Test Analysts who work at the Team level will focus on performing system testing on new and existing functionality in a sandboxed environment to ensure that it is functioning properly. Through a fully automated continuous delivery pipeline, the team will get fast, reliable feedback.

At the Program level, organizations will perform system integration testing (SIT) to verify working features and functionalities that were delivered by more than one team. Who should execute at this level of testing? Putting this responsibility on members at the Team level would greatly reduce the teams’ delivery velocity. Taking system integration testing responsibilities away from these teams allow them to focus on their main system.
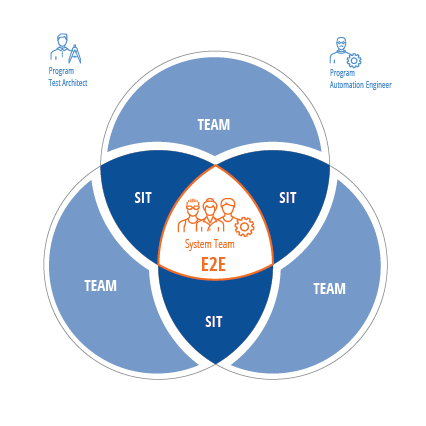
The System Team will execute system integration test scenarios that run across multiple teams, applications, or processes. These scenarios are assembled from test artifacts created at the Team level.
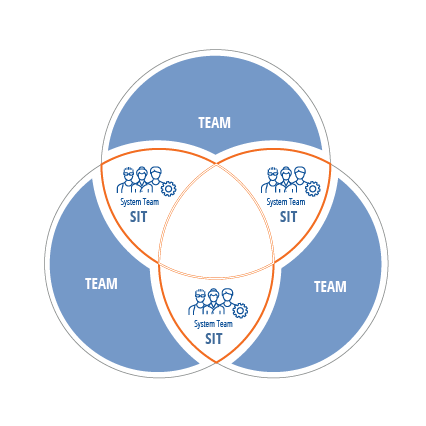
To ensure testing is streamlined, organizations should designate specific roles to coordinate and execute these tests.
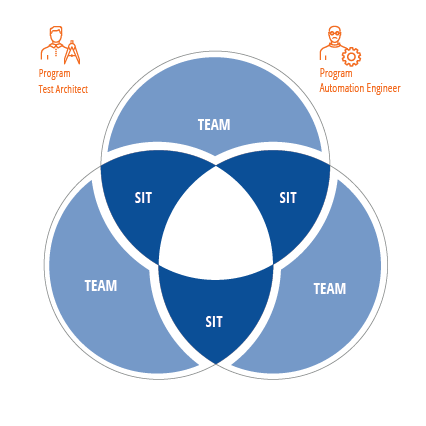

At the Enterprise level of CTF, an organization seeks to establish end-to-end (E2E) testing. This important testing type sits in the center of testing activities and will be closest to the expected user experience.
Once an organization has coordinated testing across multiple teams, it is well on the way to achieving end-to-end testing. At this point, there are still no formal guardrails at the Enterprise level to ensure that the right people are using the right tools as they work within the defined testing strategy. To address strategic decisions and to continuously improve the guardrails, it’s essential for organizations to form an Enterprise Enablement team.
The Enterprise Enablement Team is usually made up of experts taken from various teams throughout the organization.
These roles are
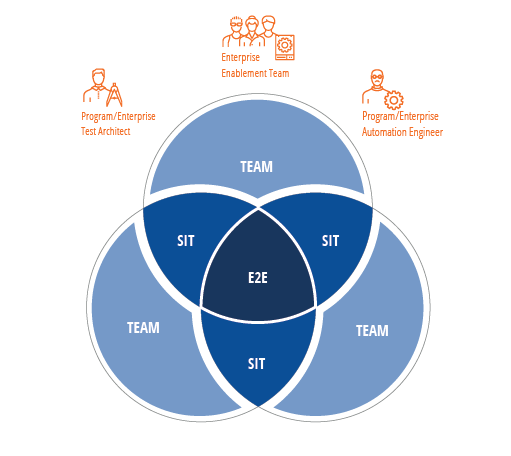
Together, these professionals provide testing expertise in a shared services model, often through a services catalog that is available to any team that needs assistance:
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE ENTERPRISE ENABLEMENT TEAM
In addition, the System Team will work at the Enterprise level, but with a different scope than at other levels. At the Enterprise level, organizations will require fewer tests, but the tests will be more complex because they will simulate, even more, the customer experience and processes. The System Team will execute these tests. To ensure that they can complete the tests quickly and on schedule, they reuse testing artifacts.

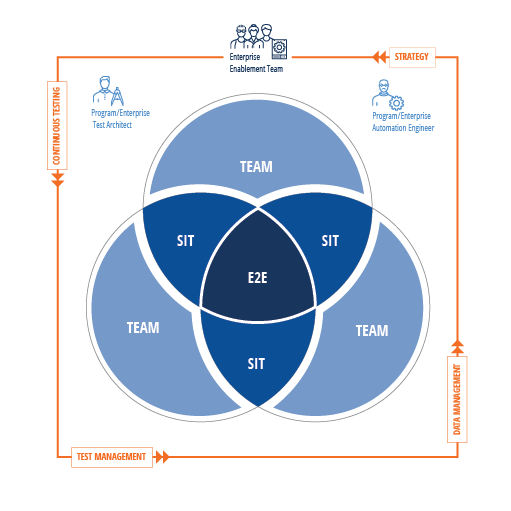
As an organization scales up continuous testing and adopts agile methodologies, it may set goals of increasing efficiency and reducing costs. It should also aim to foster learning and sharing across its teams, so that as many teams as possible can grow and improve from modern testing practices.
You can amplify continuous learning and improvement by:
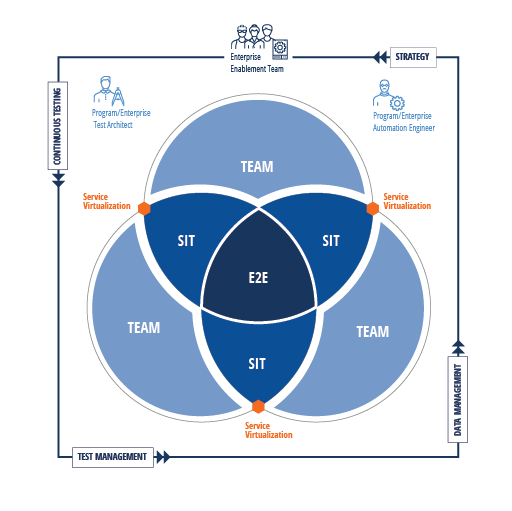
By establishing feedback loops and emphasizing constant improvement of their testing practices, organizations can make steady progress towards continuous testing.
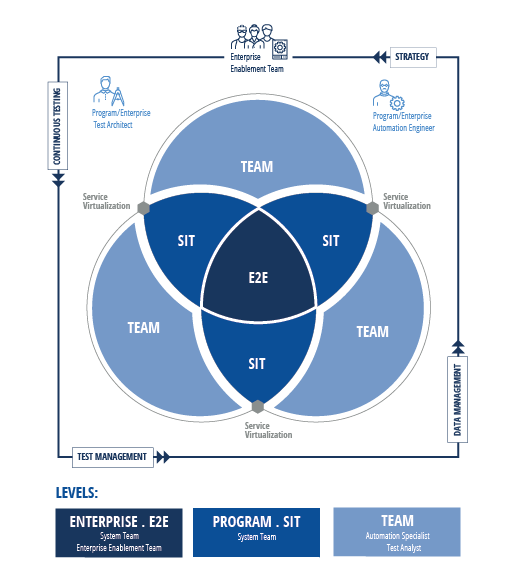
Collaboration is an essential—yet often overlooked—component of a high-performing development organization. When your organization collaborates at the Team, Program, and Enterprise levels, you can amplify continuous learning and drive steady improvement of your testing processes.

Watch this webinar to hear two Tricentis experts discuss what’s...


Integrate observability into performance testing to catch issues...

Explore how Tricentis AI Workspace enables autonomous quality at...

From agentic AI to API simulation, Tosca’s cloud deployment is...

Learn how AI-driven quality intelligence transforms QA to test what...