

In 2023, hackers discovered a security vulnerability in MOVEit, a file transfer software used by many organizations around the world. This allowed them to steal sensitive data from both companies and third-party vendors, showing how one overlooked vulnerability can lead to massive damage.
Incidents like this show why security testing is important. It helps you find and fix weak points early, reduce risk, and stay protected against real-world threats.
“It takes 20 years to build a reputation and a few minutes of a cyber-incident to ruin it.” – Stéphane Nappo, Global CISO, Groupe SEB
In this post, we’ll cover the basics of security testing, why it’s important, the different types, how to implement it, and some best practices to follow.
What is security testing?

Security testing is the process of checking a software application to find and fix vulnerabilities that attackers could use to gain unauthorized access. Its goal is to ensure that the system protects sensitive data and remains reliable against malicious threats.
This is important because:
- It protects sensitive information, such as personal user data and financial details, from unauthorized access.
- It identifies vulnerabilities early in the development process.
- It helps prevent attacks that could compromise the system’s ability to function well.
- It helps to maintain user and customer confidence in the software and organization.
- It helps to improve the overall quality and reliability of software applications.
In essence, security testing involves simulating attacks, checking security features, and verifying compliance with security standards to find and fix potential risks before they cause damage.
Principles of security testing
Security testing is based on a few key principles that guide how we protect software and systems from attacks. These principles help to make sure that data stays safe, users are who they claim to be, and systems work as expected.
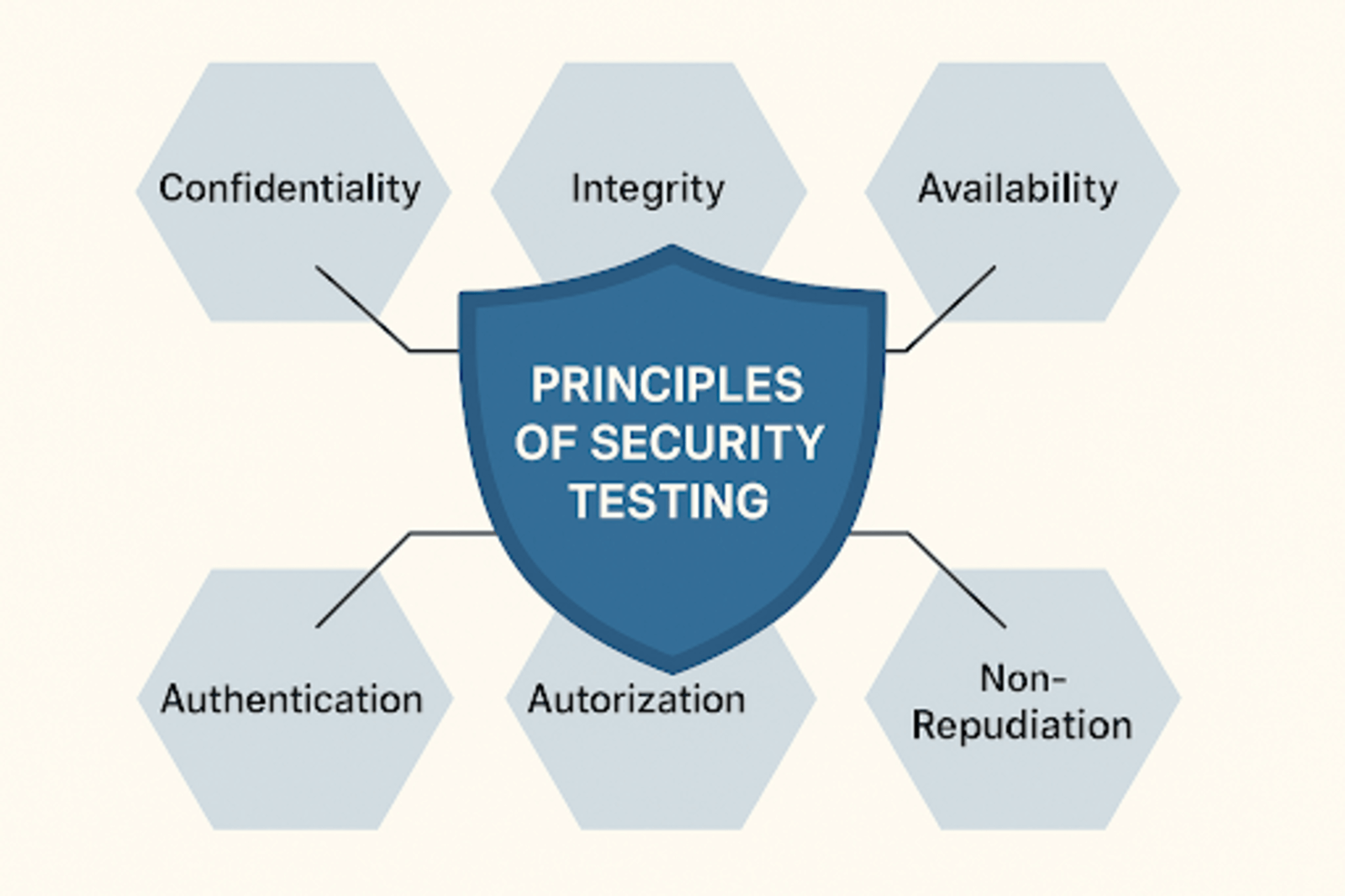
1. Confidentiality
Confidentiality means keeping sensitive information private and ensuring that only authorized users can access it. Security testing checks that data like passwords and other personal and business information are not exposed to unauthorized users.
2. Integrity
Integrity ensures that data is accurate and has not been tampered with by unauthorized users. Security testing verifies that information remains consistent and trustworthy.
3. Availability
Availability means that the system and its data are accessible when authorized users need them. Security testing looks for weaknesses that could cause downtime or denial of service. It ensures the system remains reliable.
4. Authentication
This verifies the identity of users or systems before granting access. Security testing confirms that authentication mechanisms (like passwords, biometrics, or tokens) are strong and effective.
5. Authorization
Authorization controls what authenticated users are allowed to do. It ensures users can only access resources and perform actions they have permission for. Security testing checks that access controls are properly enforced.
6. Non-repudiation
This ensures that users can’t deny actions or transactions after they have been performed. Security testing verifies that systems keep reliable logs and evidence so users cannot falsely deny their activities.
Types of security testing
There are various ways to identify and fix security problems in software applications. Each of them focuses on different aspects of security.
Vulnerability scanning
This uses automated tools to scan systems, applications, or networks for known security problems. It compares these problems against databases of known vulnerabilities. This helps to prioritize fixes based on severity.
The goal of penetration testing is to identify potential weaknesses before an attacker does – and then develop ways to fix those weaknesses
Penetration testing (Pen testing)
According to John Boardman, “The goal of penetration testing is to identify potential weaknesses before an attacker does – and then develop ways to fix those weaknesses.”
It involves ethical hackers simulating real attacks to find security issues that automated tools might miss. This reveals how vulnerabilities can be exploited and their potential impact.
Application security testing
This is a broad category that focuses on identifying security issues in software applications. It includes several approaches:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Analyzes source code or binaries without running the application to find coding errors and vulnerabilities early in development.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Tests running applications by simulating attacks to detect runtime vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting.
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST): Combines SAST and DAST by monitoring the application during execution to provide real-time vulnerability detection.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): Examines third-party and open-source components used in applications to identify known vulnerabilities.
- Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST): Focuses specifically on mobile apps (Android, iOS). It addresses unique risks like insecure data storage, improper API usage, and platform-specific threats.
Additionally, platforms like Tricentis Vera can help ensure that compliance and security policies are enforced across the development and testing workflows, thus reducing audit risk or manual effort.
Web application testing
A specialized form of application security testing that only targets web apps. It focuses on finding vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and broken authentication.
API testing
This involves testing APIs for weaknesses such as improper authentication and data leaks. It ensures secure communication between software components. You can use Postman and SoapUI for API testing.
Risk assessment
Risk assessment evaluates potential threats to systems and data, estimating the likelihood and impact of each risk. Not only that, risk assessments also help organizations prioritize security efforts by focusing on the most critical threats.
Network security testing
Focuses on testing network infrastructure, including firewalls, routers, and servers, for vulnerabilities like open ports, weak protocols, or misconfigurations. Tools like Nmap, Wireshark, and Netcat are used to map networks and identify potential entry points for attackers.
Ethical hacking
This is the practice of authorized professionals attempting to breach systems to find security flaws before malicious hackers do. It often overlaps with penetration testing but can be broader. It involves social engineering, physical security testing, and more.
How to carry out security testing
Here are the key steps to help you plan, execute, and manage security testing successfully:
- Define the scope: Decide what you’re testing. This could be a specific feature or a whole application. Understand the regulatory standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or ISO 27001, and identify the specific risks associated with your application.
- Gather information: Learn how the system works. Understand its components, architecture, and data flow. Check how the app handles inputs, authentication sessions, and data storage. This step will help you spot where security issues are likely to happen.
- Identify possible threats and vulnerabilities: In this step, you need to think like an attacker. What would they target? Is there a risk of SQL injection, XSS, or weak authentication? These are some of the questions you ask yourself.
- Choose your testing methods and tools: Select the type of testing that fits your goals, like vulnerability scanning, pen testing, etc. After that, you pick the right tools to support your work. Examples are OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, Snyk, Nessus, etc.
- Run the tests: Execute the tests you planned, both automated scans and manual checks. Try to simulate real-world attacks to see how the system responds. Also, keep logs of everything for later review.
- Analyze the results: Review the test findings to understand which vulnerabilities are real, how severe they are, and how they could be exploited. Prioritize high-risk issues that affect sensitive data or critical features.
- Report and fix the issues: Document the vulnerabilities clearly—what they are, where they happen, and how to fix them. Then work with your team to patch the problems. Don’t forget to include screenshots, URLs, and payloads for clarity.
Start security testing immediately when you start development and continue to test throughout the development cycle
Security testing best practices
It’s important that you follow some best practices to make security testing more effective. These ensure that your application is secure and reliable.
- Start early and test often: Start security testing immediately when you start development and continue to test throughout the development cycle. Early testing helps catch issues before they become obvious and expensive to fix.
- Combine manual and automated testing: Automated tools can quickly scan your system for errors, but manual testing by skilled security experts can find complex or hidden issues that tools might miss.
- Stay up-to-date with the latest security trends: Hackers always look for various ways to access systems. Staying updated will help you update testing techniques and tools.
- Document findings and remediation steps: Keep a record of all the vulnerabilities you discover and prioritize them. Clear documentation helps development teams understand and address issues efficiently.
Tools like Tricentis Tosca support the best practices listed above. It does so by enabling traceable audit workflows and automated security validations across the SDLC.
Conclusion
Security testing is a vital part of software development that helps identify and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. By understanding key principles, using various testing types, and following best practices, organizations can protect their systems and sensitive data from cyber threats.
According to Kevin Mandia (CEO of Mandiant), “If you aren’t investing in cybersecurity, you’re investing in vulnerability.” So, make security testing a regular part of your development process to create safer, more reliable software.
This post was written by Chosen Vincent. Chosen is a web developer and technical writer. He has proficient knowledge in JavaScript, ReactJS, NextJS, React Native, Node.js, and databases. Aside from coding, Vincent loves playing chess and discussing tech-related topics with other developers.
